10166. Max-heap
Given an array of integers. Rearrange its elements to form a max-heap.
Input. The first line contains the number of elements in the array n (n
≤ 1000).
The second line contains n integers, each with an absolute value
not exceeding 106.
Output. Print the rearranged array representing a max-heap. If
there are multiple solutions, print any one of them.
|
Sample input |
Sample output |
|
6 5 3 2 7 1 10 |
10 7 5 3 1 2 |
SOLUTION
heap
Algorithm analysis
Store the input data in an array a. For all
indices from n / 2 down to 1, apply the heapify procedure
in sequence. As a result, the array will be transformed into a max-heap.
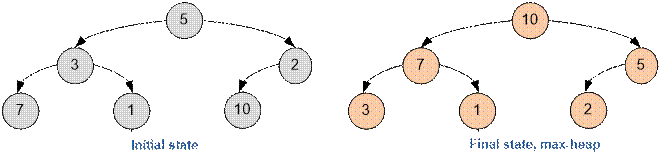
Example
Below are
the initial array and the final array that represents a heap.
Algorithm implementation
Declare an
array that will later be transformed into a heap.
#define MAX 1001
int a[MAX];
The left function
returns the index of the left son.
int left(int i)
{
return 2 * i;
}
The right function
returns the index of the right son.
int right(int i)
{
return 2 * i + 1;
}
The swap function
exchanges the elements at indices i and j.
void swap(int &i, int &j)
{
int temp = i; i = j; j = temp;
}
The heapify function
restores the heap property for the subtree rooted at the node with index i. The third parameter n defines the size of the
maintained heap.
void heapify(int a[], int i, int n)
{
int largest = 0;
int l = left(i);
int r = right(i);
Find the index of the largest element among the current
element a[i] and its children a[l] and a[r].
if (l <= n && a[l] > a[i]) largest = l;
else largest = i;
if (r <= n && a[r]
> a[largest]) largest = r;
If a[i] is not the largest element, swap it with
the largest son and then
recursively restore the heap property in the corresponding subtree (left or
right).
if (largest != i)
{
swap(a[i], a[largest]);
heapify(a, largest,
n);
}
}
The main part
of the program. Read the
input array starting from index 1.
scanf("%d", &n);
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++)
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
For all indices from n / 2 down to 1, perform the heapify procedure in sequence.
for (i = n / 2; i > 0; i--)
heapify(a, i, n);
Print the
resulting array, which represents a max-heap.
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++)
printf("%d ", a[i]);
printf("\n");
Java implementation
import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
static int left(int i)
{
return 2 * i;
}
static int right(int i)
{
return 2 * i + 1;
}
static void
swap(int a[], int i, int j)
{
int temp = a[i]; a[i] = a[j]; a[j] = temp;
}
//max - heap
static void
heapify(int a[], int i, int n) // n = size of a heap
{
int largest = 0;
int l = left(i);
int r = right(i);
if (l <= n && a[l] > a[i]) largest = l;
else largest = i;
if (r <= n && a[r] > a[largest]) largest = r;
if (largest != i)
{
swap(a, i, largest);
heapify(a, largest, n);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner con = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = con.nextInt();
int m[] = new int[n+1];
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
m[i] = con.nextInt();
for(int i = n / 2; i > 0; i--)
heapify(m,i,n);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
System.out.print(m[i] + " ");
System.out.println();
con.close();
}
}